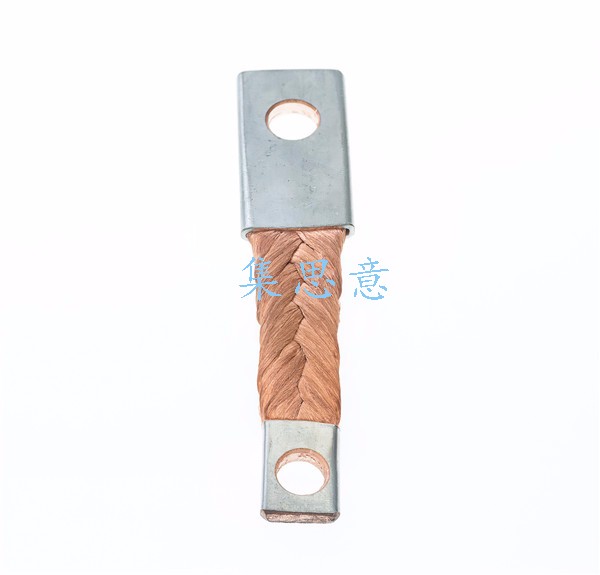
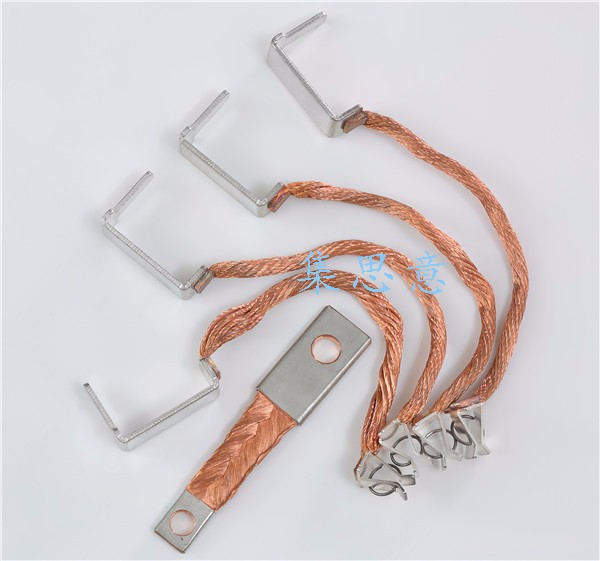
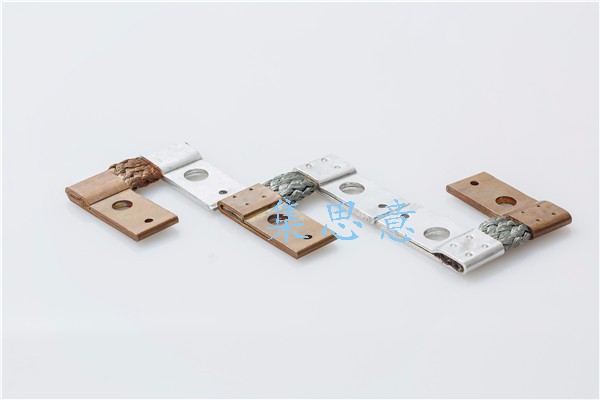
Which is the stronger of the current carrying capacity of copper braided wire, copper bar and copper cable
Copper braided wire copper bar and copper cable are generally used as copper conductor for connection of various equipment. Which is the stronger current carrying capacity? Jisiyi special braided wire Co., Ltd. tells you three principles for selecting Copper Conductor:
1. For short distance and small load, the conductor section (safe carrying capacity) shall be selected according to the heating conditions, and the current shall be controlled by the heating conditions of the conductor. The smaller the section area is, the better the heat dissipation is, and the greater the current passing through the unit area is.
2. On the basis of safe carrying capacity of long-distance and medium load, the conductor section shall be selected according to the condition of voltage loss. It is not enough for long-distance and medium load only not to heat, but also to consider the voltage loss. To ensure that the voltage to the load point is within the qualified range, the electrical equipment can work normally.
3. On the basis of qualified safe current carrying capacity and voltage drop, large load should be selected according to economic current density, that is, power loss should be considered, and power loss and capital investment should be in the most reasonable range. Safe carrying capacity of conductor? In order to ensure the continuous operation of the conductor for a long time, the allowable current density is called safe carrying capacity.
The general current carrying capacity is as follows:
2-5A / mm2 for copper braided wire;
Copper bar selection 2.5-3a / mm2;
2.5-4a / mm2 for copper cable.
The safe carrying capacity should be determined according to the limit temperature, cooling conditions, laying conditions and other comprehensive factors. Generally, short distance, small cross-sectional area, good heat dissipation, low temperature, strong conductor conductivity, upper limit of safe current carrying; long distance, large cross-sectional area, poor heat dissipation, high temperature, poor natural environment, weak conductor conductivity, lower limit of safe current carrying; such as conductivity, bare conductor is stronger than insulated wire, overhead wire is stronger than cable, and buried cable is stronger Cables laid on the ground, etc.
1. For short distance and small load, the conductor section (safe carrying capacity) shall be selected according to the heating conditions, and the current shall be controlled by the heating conditions of the conductor. The smaller the section area is, the better the heat dissipation is, and the greater the current passing through the unit area is.
2. On the basis of safe carrying capacity of long-distance and medium load, the conductor section shall be selected according to the condition of voltage loss. It is not enough for long-distance and medium load only not to heat, but also to consider the voltage loss. To ensure that the voltage to the load point is within the qualified range, the electrical equipment can work normally.
3. On the basis of qualified safe current carrying capacity and voltage drop, large load should be selected according to economic current density, that is, power loss should be considered, and power loss and capital investment should be in the most reasonable range. Safe carrying capacity of conductor? In order to ensure the continuous operation of the conductor for a long time, the allowable current density is called safe carrying capacity.
The general current carrying capacity is as follows:
2-5A / mm2 for copper braided wire;
Copper bar selection 2.5-3a / mm2;
2.5-4a / mm2 for copper cable.
The safe carrying capacity should be determined according to the limit temperature, cooling conditions, laying conditions and other comprehensive factors. Generally, short distance, small cross-sectional area, good heat dissipation, low temperature, strong conductor conductivity, upper limit of safe current carrying; long distance, large cross-sectional area, poor heat dissipation, high temperature, poor natural environment, weak conductor conductivity, lower limit of safe current carrying; such as conductivity, bare conductor is stronger than insulated wire, overhead wire is stronger than cable, and buried cable is stronger Cables laid on the ground, etc.